- Faris Delija
- April 2021
- Uncategorized
In this post we explore the backbone of all operations in SAP Business One – Master Data. The system’s corresponding element lets you adjust the information about your partners, clients, and products and store it most efficiently. The following material sheds light on how to use Master Data in SAP Business One, including SAP Master Data creation and management processes. Besides, we shed light on how to set up predefined values and defaults for master data in SAP Business One. Since Business Partner Master Data and Item Master Data creation is a complex process, we give special consideration to it via two separate articles.
SAP Business One master data use principles
You have partners divided into three groups (customers, vendors, and leads), items stored in the inventory, and G/L accounts utilized in transaction posting. SAP Business One lets you store them using specific master data records. Every time a new document is created within the system or other actions occur, the software provides much of the required information with the help of these entries.
At the same time, master data is responsible for predefined values and numerous settings that automated wizards use to establish payment processing, dunning activities, and material requirements planning.
While default control accounts of vendors, customers, and items are considered master data, more information is required to describe the associated transactions. Here, transactional data enters the game. It characterizes actions applied to master data records, such as purchase order creation for a particular vendor.
In their turns, documents in SAP Business One can contain information associated with a set of master data records. Imagine a purchase order that consists of multiple items, warehouse shipping address, payment method, and various contact details. As for the transactional data, it describes what to do with this information.
So, why should you set up master data correctly? The answer is obvious: you simplify all further actions that take place in SAP Business One. The proper setup dramatically enhances the efficiency of your daily chores. Accurately configured master data reduces the complexity of document creation to confirming that the current information is correct.
On the other hand, inaccurate master data disrupt business processes and may lead to severe consequences and money losses. Let’s see how to use master data in SAP Business One to avoid this scenario.
SAP B1 Master Data Records
Business partners and items are the main two categories of SAP Business One master data. The business partner category, in its turn, is divided into the following three groups:
- Lead data is used to describe your potential customers – various people and organizations in the sales pipeline. Such records form the background for sales and marketing campaigns. When a lead makes their first purchase, the system transfers them to the new dimension – customers.
- Customer data is utilized to distinguish people and organizations you work with while selling products and services. The corresponding records participate in documents related to processing and fulfilling orders.
- Vendor data, in its turn, is associated with the people and organizations from which you buy products and services. It takes part in creating documents related to purchasing, accepting delivery, and processing payments to vendors.
Additional master data types include resources, fixed assets, serial numbers, etc. We will also shed light upon them in the framework of your SAP Business One In-depth Review. Now, let’s return to our mutton.
Because data records associated with leads, customers, and vendors are always similar, SAP Business One utilizes a common window for each record type. The Business Partner Master Data screen looks as follows:
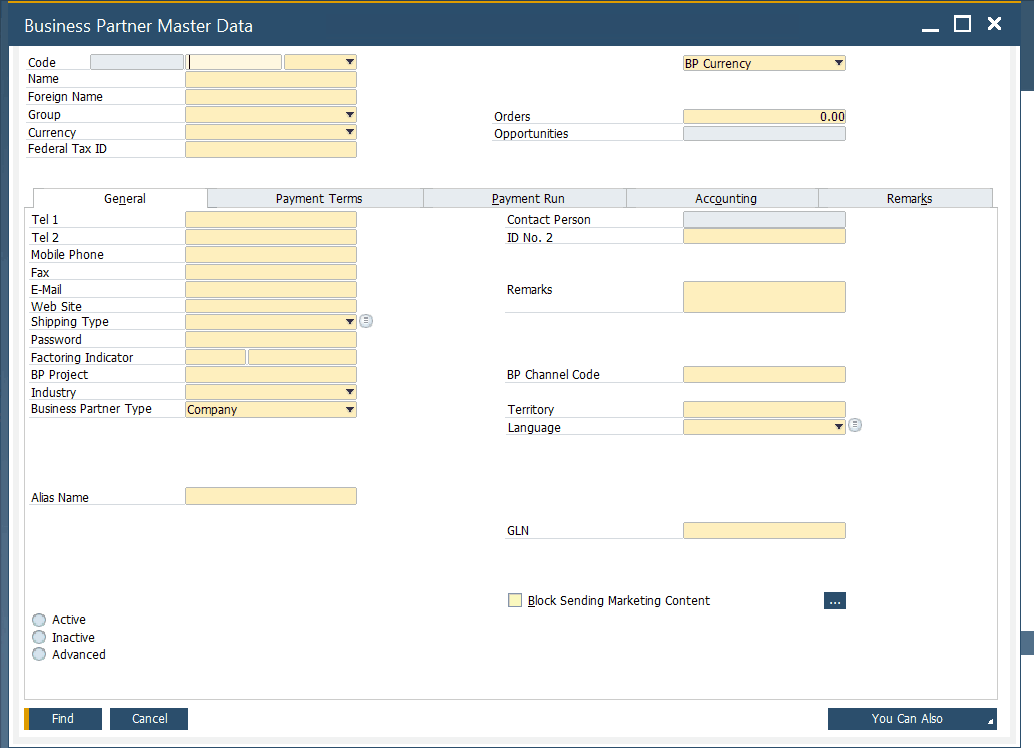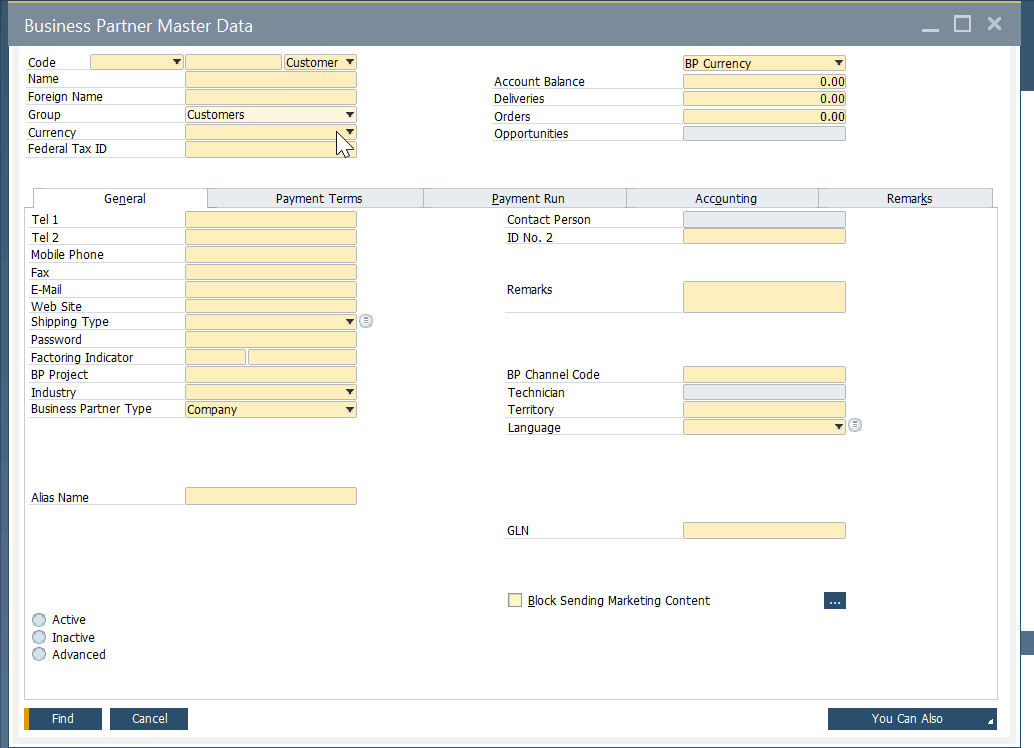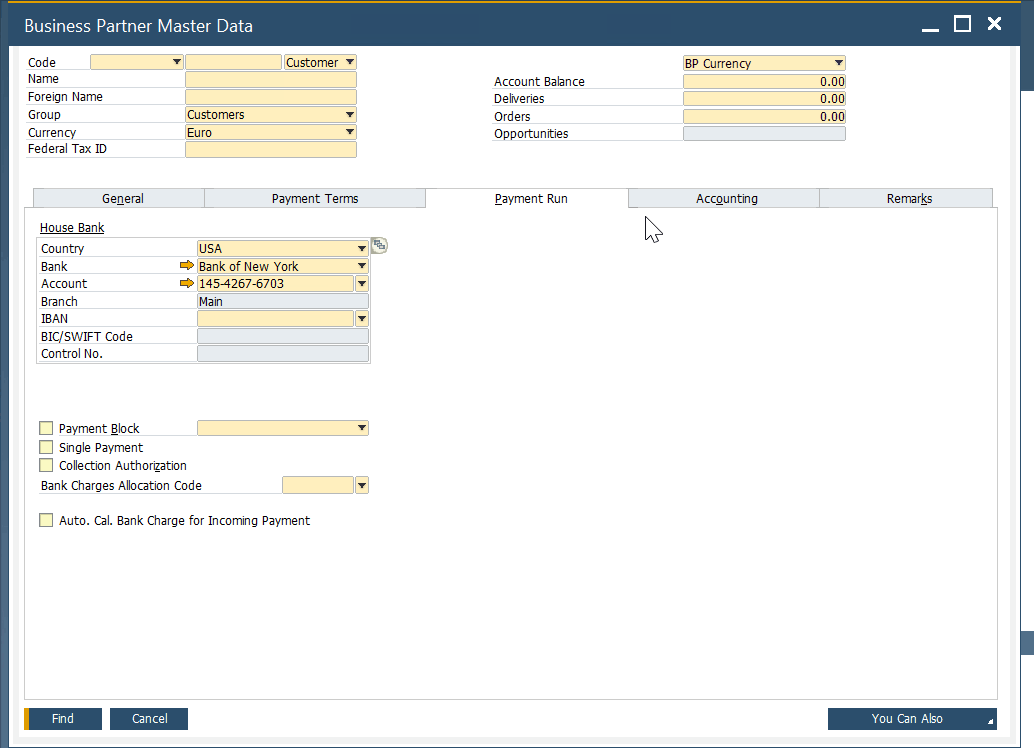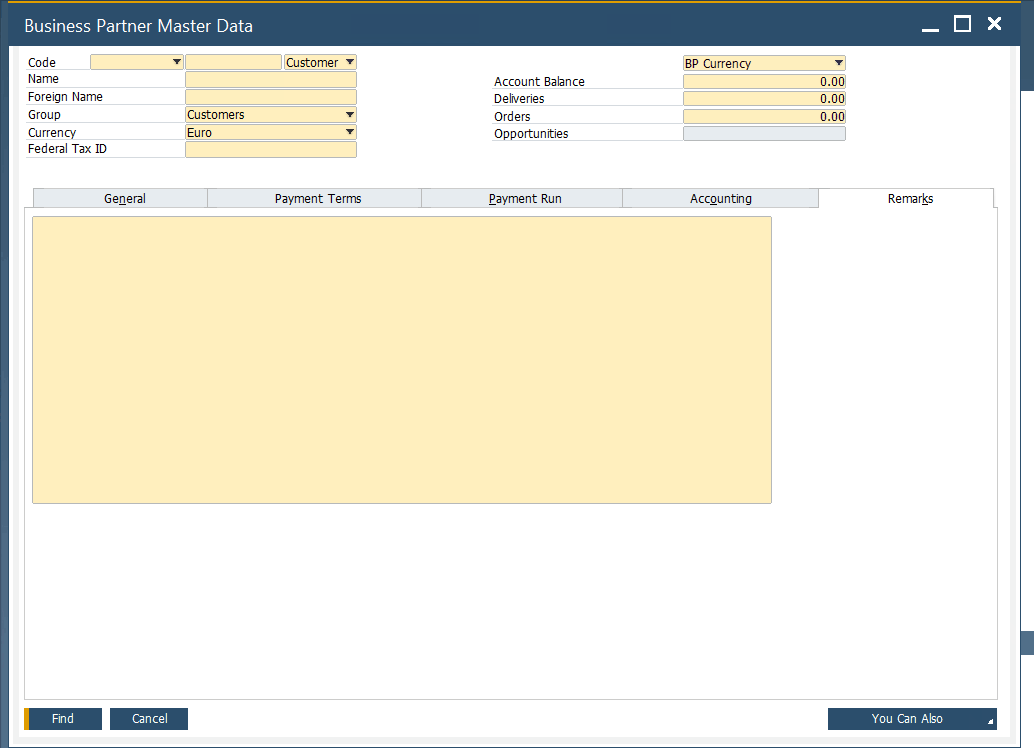
As you can see, all the basic information is located in the header, including the business partner name, group, currency, tax ID, account balance, orders, and category (lead, customer, or vendor). Several tabs below keep track of different business partner information. We will describe all of them in more detail in another article.
As for an item master data window, it has a very similar appearance: the header section with the basic information and tabs below. SAP Business One uses item master records to create sales quotations, POs, bills of materials, and documents necessary for moving goods in and out of your enterprise. Here is how an item master data screen looks:
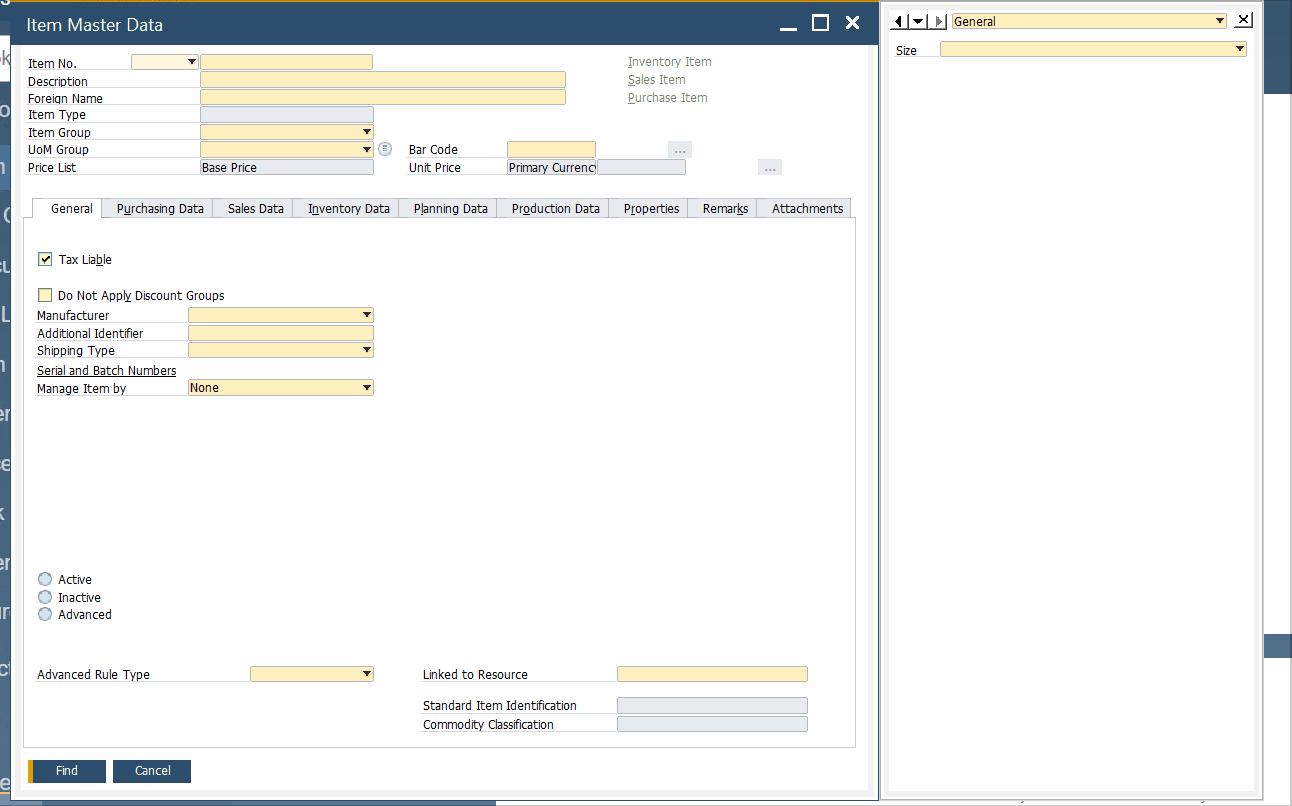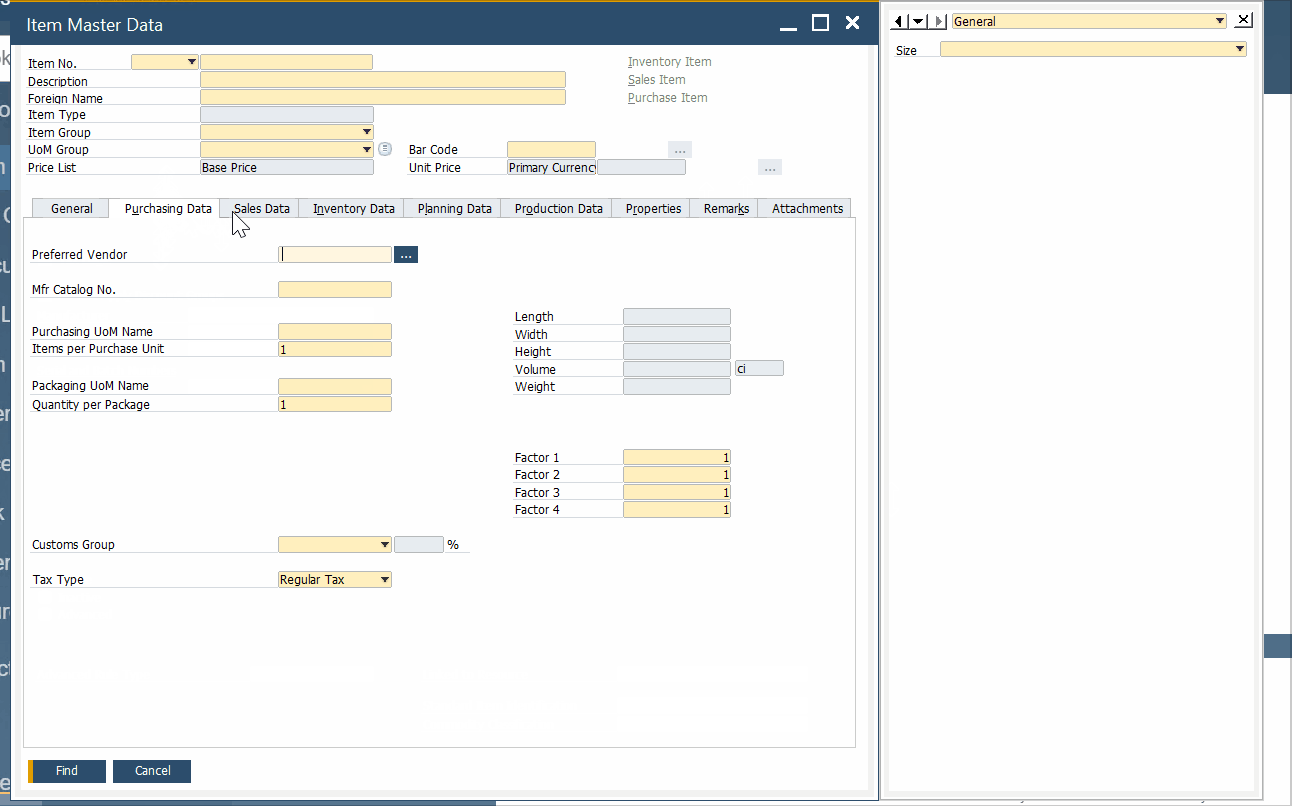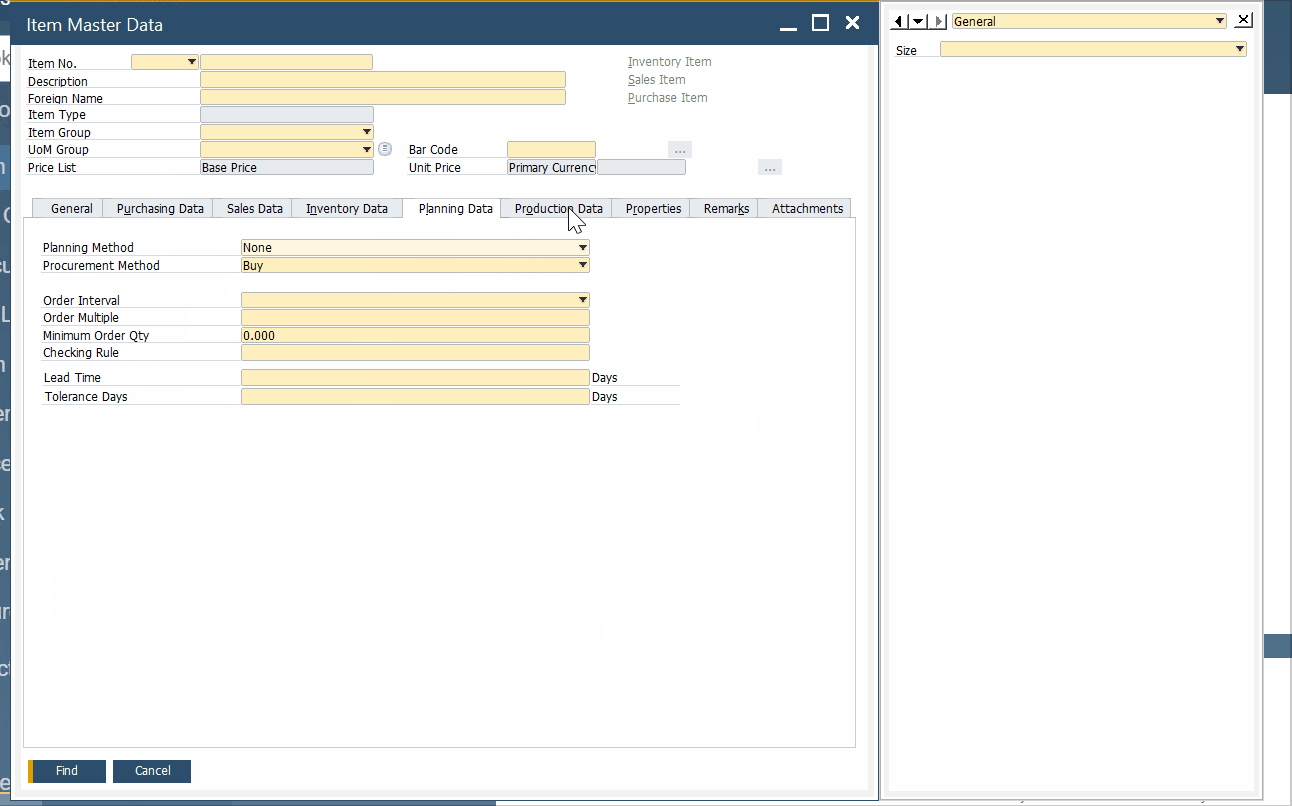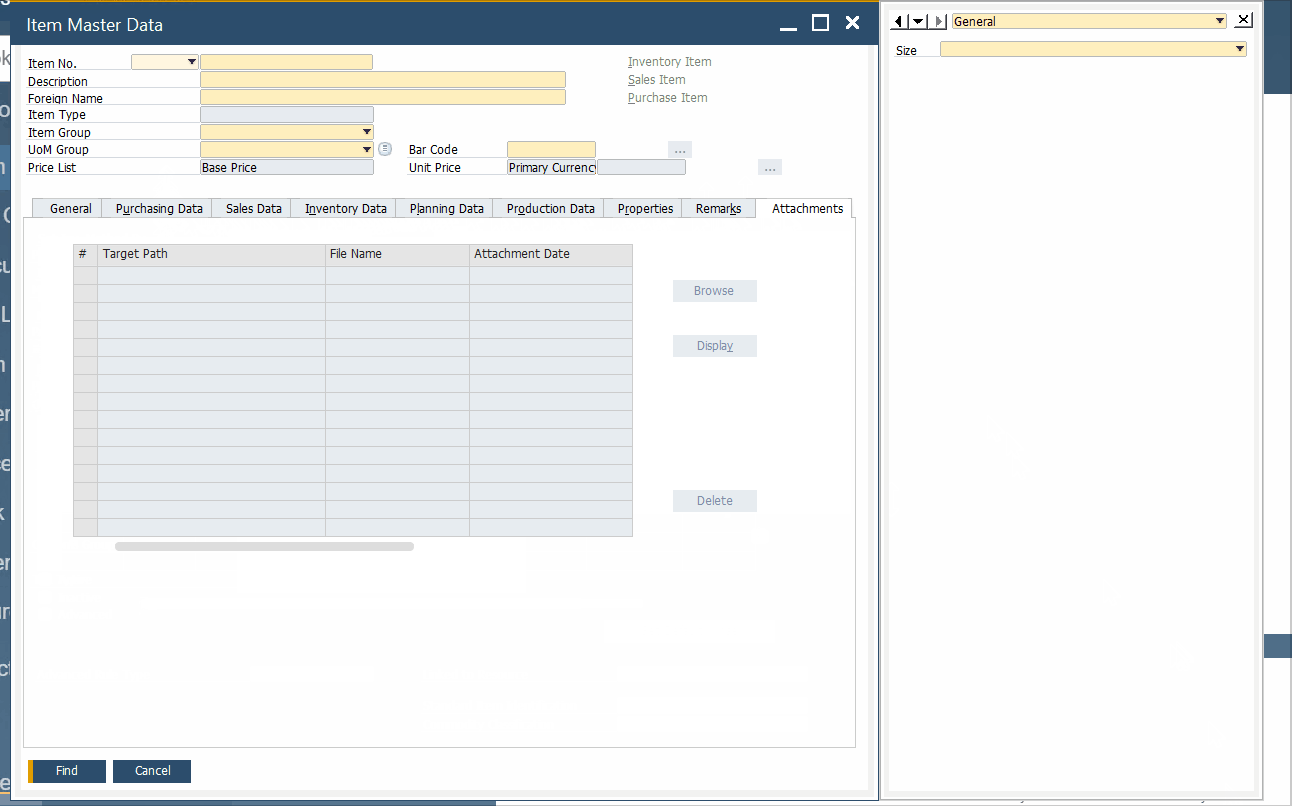
SAP Business One uses item data records to store the following information:
- how the item may be purchased or sold;
- the item price;
- the inventory level;
- the item purchase forecast or plan.
The ERP system delivers fully-fledged flexibility for item master data by supporting a two-way process. While some items are sold by your company, the others may be purchased. At the same time, some of them may be fixed assets tracked for accounting purposes only. SAP Business One lets you manage all of them within the same interface.
It is also worth mentioning that there are situations when you cannot delete master data records. If it is involved in an accounting or inventory transaction, you won’t be able to remove it from the system. Besides, all partners and items linked to a sales order are also protected.
When it comes to fixed assets, SAP B1 lets you calculate and post depreciation journal entries across fiscal years automatically. Besides, the system offers the means necessary to generate forecast reports regarding the future value of each asset.
Predefined Values and Defaults
Now, let’s explore how to optimize master data records in SAP Business One. The data that populates drop-down lists and shows up in each window by default is associated with predefined values and defaults correspondingly. The former is associated with countries, vendors, customers, payment terms, items, etc. Thus, predefined values describe information that repeatedly appears in master data records and is crucial from the perspective of reporting and automation.
Adding predefined values is as simple as selecting the Define New when the drop-down list is open.
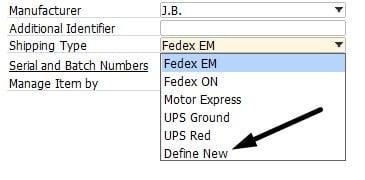
Alternatively, it is possible to go to the corresponding menu item situated under setup.
As for the default data, it is crucially important for a new master record creation. SAP Business One uses the corresponding settings to determine how to fill in the record. As a result, you get the most common payment method specified and the most probable warehouse listed. Below, you can see a section with user defaults:
SAP B1 Master Data & Documents
SAP Business One lets you create various documents, including invoices, purchase orders, shipping’s, and others, following the master data records’ information. Specify a master record that should be the foundation of the document, and the system will transfer the appropriate fields into it. As a result, you achieve the following enhancements:
- Creating documents requires less time, so you enhance your productivity;
- Automation reduces data entry errors, making your documents absolutely correct.
You can create most documents from one or more master data records in SAP Business One. Moreover, the system enables you to initiate a new document from one kind of master data record but complete it by adding others. Thus, it is possible to create a new purchase order from an item master data record. Next, you may add the vendor as well as other items.
Below, you will find out how to create a new sales order from a business partner master data record:
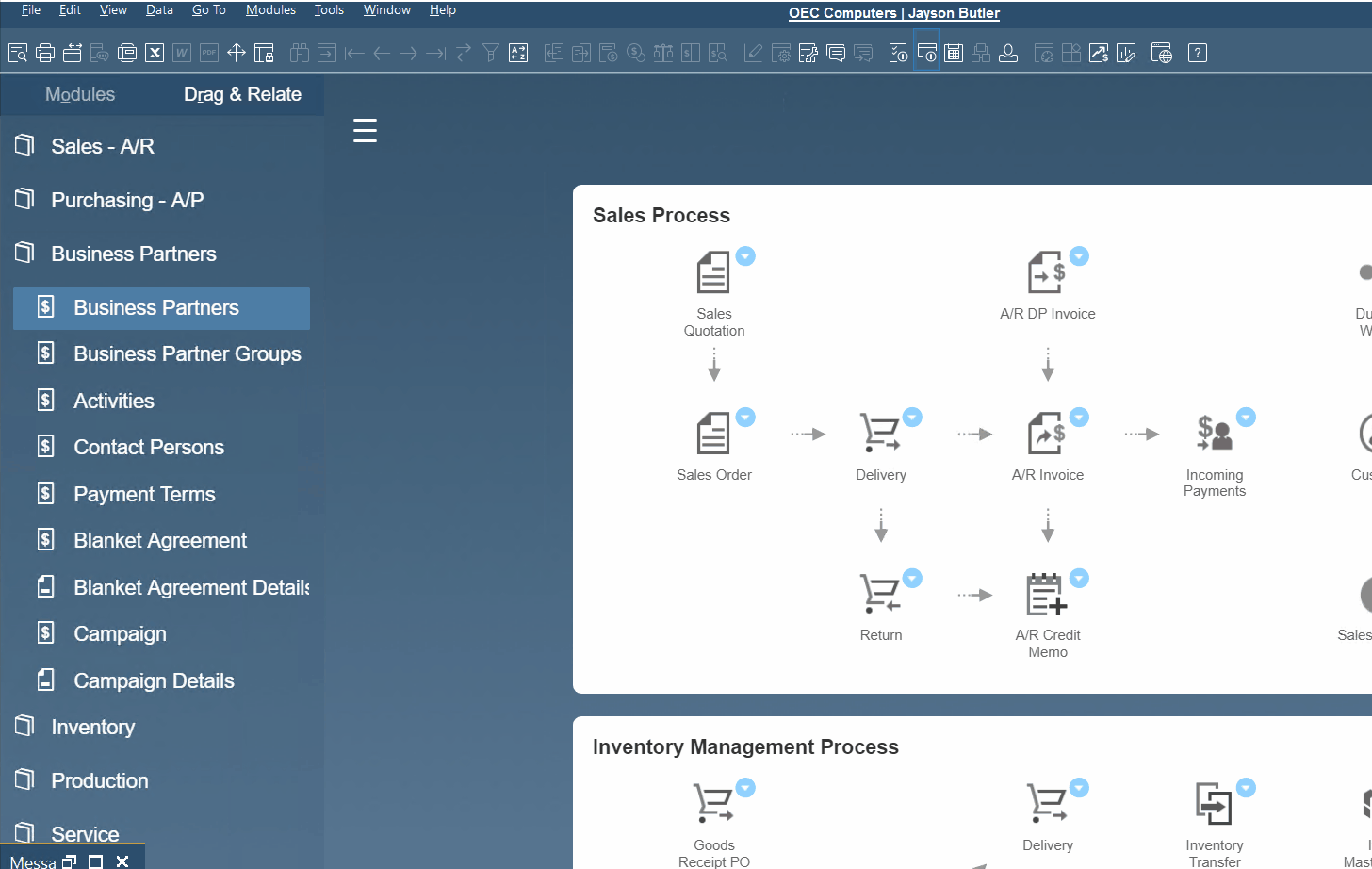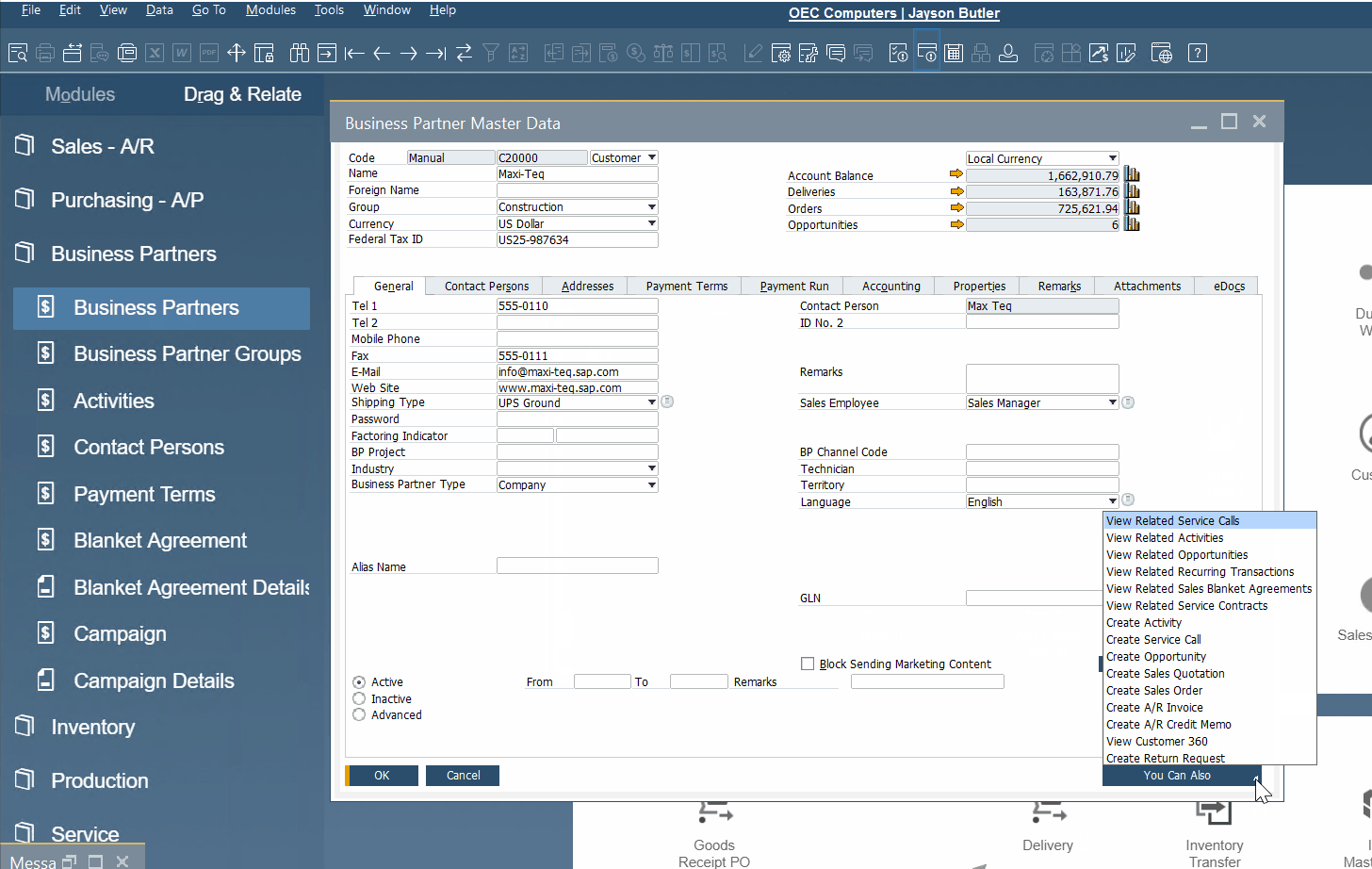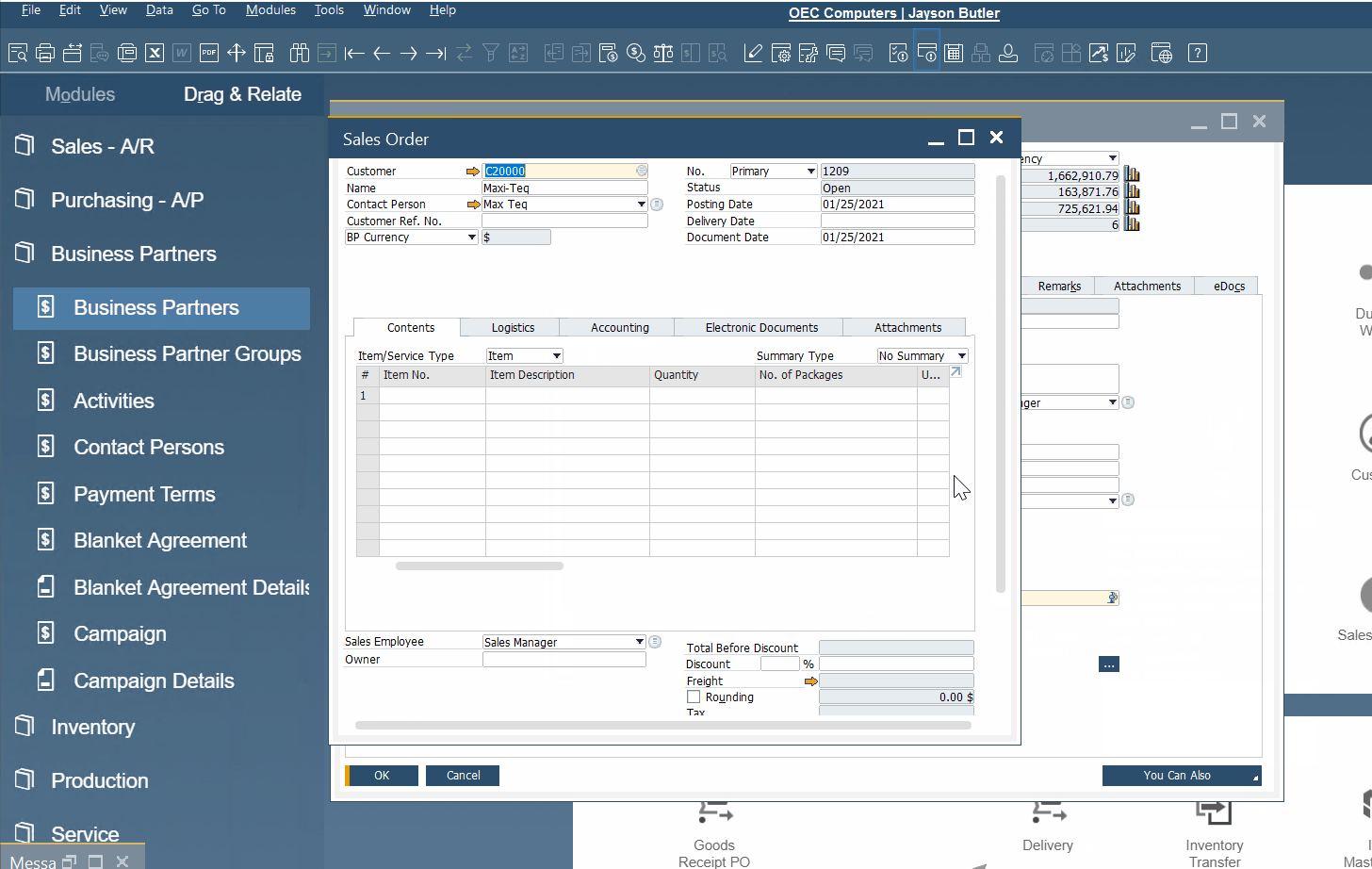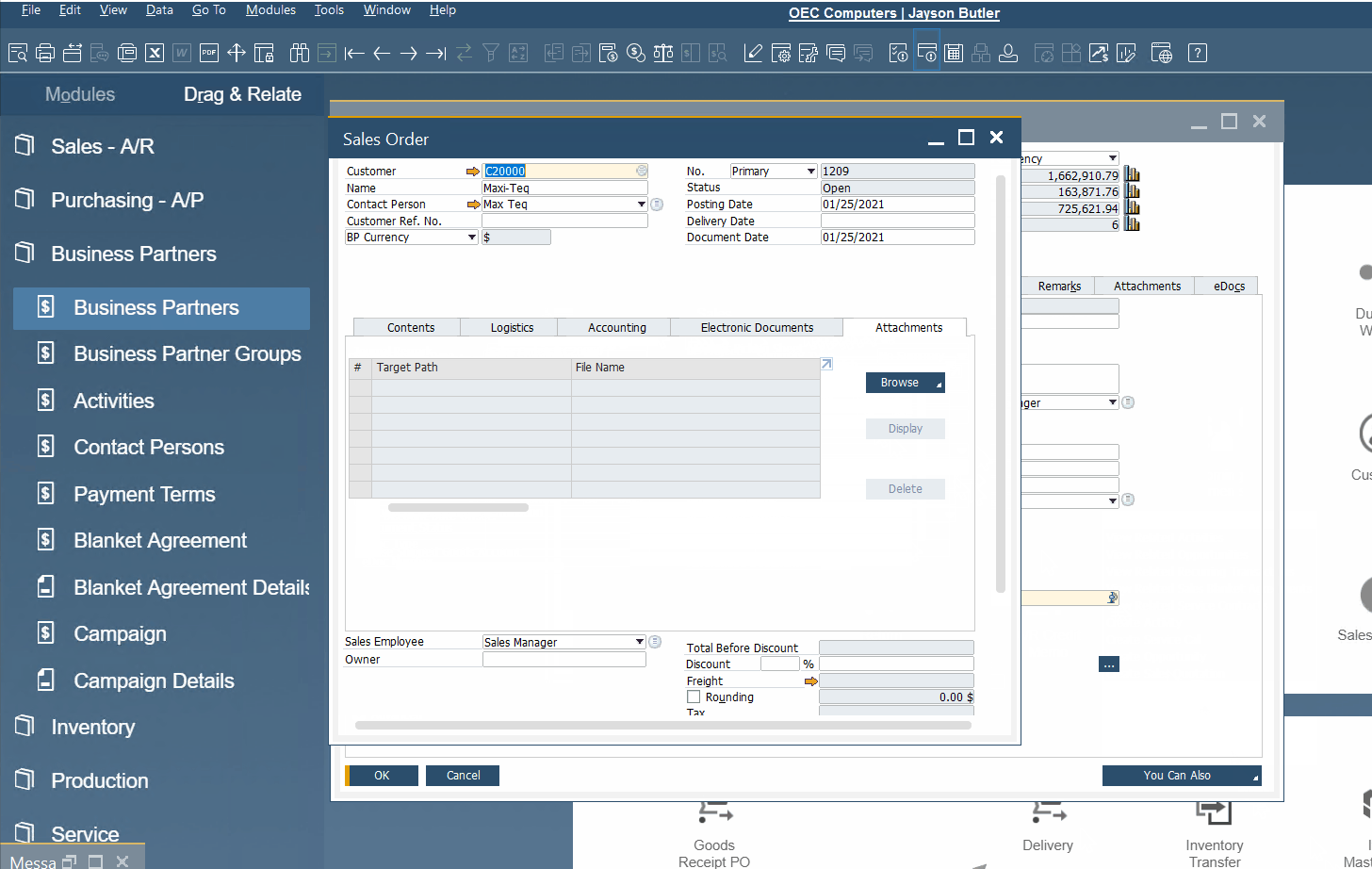
- Open the Business Partners screen under the Business Partners section of SAP B1.
- Choose a business partner master data record – click on the arrow icon.
- Hit You Can Also on the bottom right and select Create Sales Order.
- Configure your new document.
SAP B1 Master Data & General Ledger
Now, let’s say a few words about SAP B1 master data from the perspective of accounting. The ERP system creates accounting journal entries automatically. The process is synchronized with document management. For instance, every time you save a new document, a corresponding record appears in your accounting journal as follows:
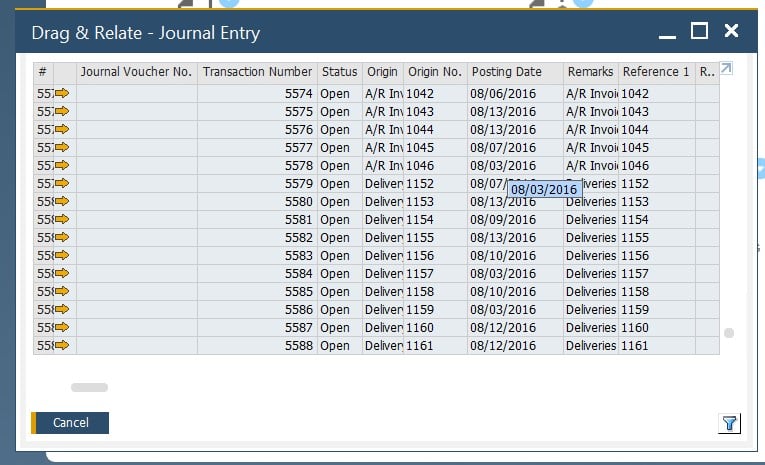
You can view each entry individually. Hit the arrow icon to proceed to its screen:
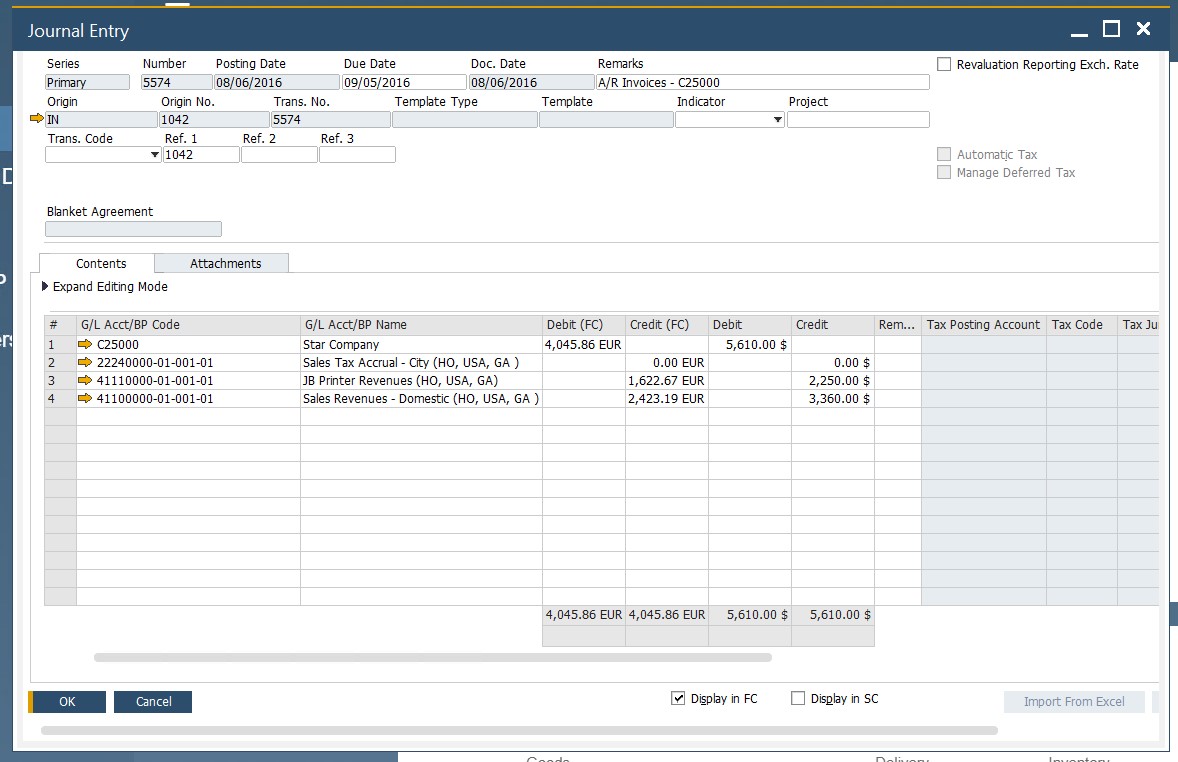
As for the general ledger automation and the SAP Business One master data role in it, we focus on this topic below.
Let’s assume that you receive an accounts payable invoice. Post it, and SAP Business One will create a new accounting journal entry that indicates an increase in accounts payable. The system discovers a control account to post it to due to the Accounting tab of a master data record. There, you can specify which account receives created journal entries by default.
In its turn, a control account is an account that represents all the business partner’s transactions in the trial balance. As we’ve just mentioned above, postings from documents associated with business partners appear there automatically.
Note that customers and vendors have slightly different control accounts. Due to the specific nature of transactions, the former can use the default accounts receivable control account. In contrast, the latter ones have default account payable controls at their service.
When you work with documents that create a journal entry, SAP Business One lets you replace the default control account for an individual transaction. Thus, it is possible to separate specific transactions without changing the master data.
SAP B1 Master Data & Reporting
And it is obvious that master data and reports are tightly connected. The Group and Properties fields of both partner and item master data records enable the classification of data you store. As a result, reports get additional flexibility. Due to various general-purpose properties stored in master data, SAP Business One also lets you streamline reporting capabilities to the maximum. Thus, the platform’s reporting mechanisms enable you to use various classifications to select and aggregate data. Note that it is possible to create custom properties to increase the default detail degree level. For instance, an item property allows for reporting on how items were introduced in a specific year. A business partner property lets you create reports for retailers from wholesalers separately.
Below, you can see a price report screen that requires both item and business partner master data records. Create a range of items and partners to see a detailed review.
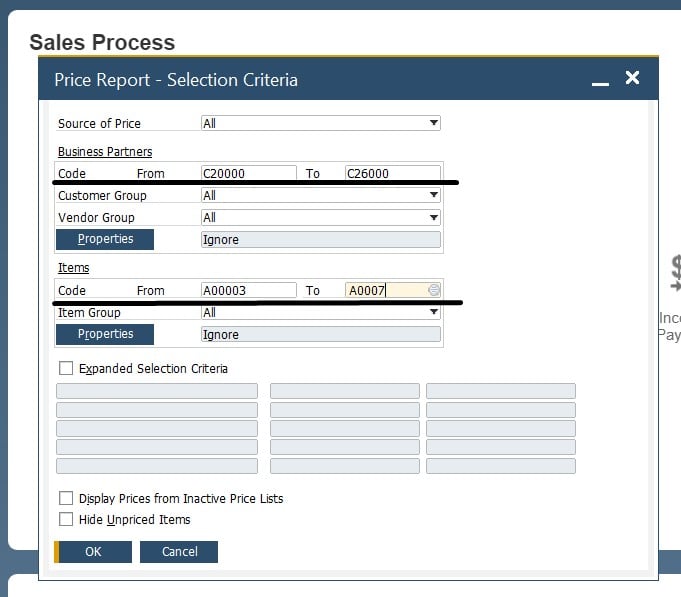
Before setting up any master data, it is recommended to consider the types of information you need in your reports. Thus, you will use master data in SAP Business One in the most effective way.
SAP Business One Master Data Creation & Management
SAP Business One divides your duties related to master data into two broad phases. Firstly, you have to set up the master data. Secondly, it is necessary to manage it properly. Let’s briefly describe the general workflow of how to use SAP Business One master data:
- Master Data Setup. When you install SAP B1 for the very first time, you have to configure your master data as follows:
- Specify predefined values and defaults;
- Create control accounts and set up determination for your partners;
- If you have any existing data, import it into SAP Business One.
- Master Data Management. Now, when you’ve prepared the background, it is possible to run your business management routine:
- Create and edit master data records for new partners and items;
- Generate new documents;
- Enable reporting;
- Configure wizards to automate repetitive processes;
- Let the system manage accounting journal entries automatically.
- Master Data Adjustment. Don’t forget to perform quality controls and adjust predefined values and defaults. Thus, you will ensure that the existing records follow the dynamically changing conditions of your enterprise.
How to set up predefined values and defaults for SAP B1 master data
Sap Business One lets you essentially simplify the creation of new master data records and documents due to properly configured predefined values and defaults. Therefore, you have to set them up correctly to enable the opportunity to generate new docs and records within a few clicks. If your new element draws data from a master record, you may create conditions when adjusting the information is reduced to looking everything over and replacing a few items. Drop-down lists and other error-resistant methods enter the game to automate your daily duties and make new records 100% correct.
As we’ve already mentioned, you deal with predefined values in various drop-down lists, such as countries, customer groups, payment terms, etc. As for the default data, SAP Business One displays it in various fields when you create a new record or document.
The opportunities are endless since every available setting provides defaults used when master data records are created, controlling various behavior in documents and records based on master data. Let’s explore a simple example.
Open the Inventory Data tab of the item master data window. Here, you can turn on the feature that adds a given item to every warehouse automatically. Just select the checkbox to activate the enhancement.
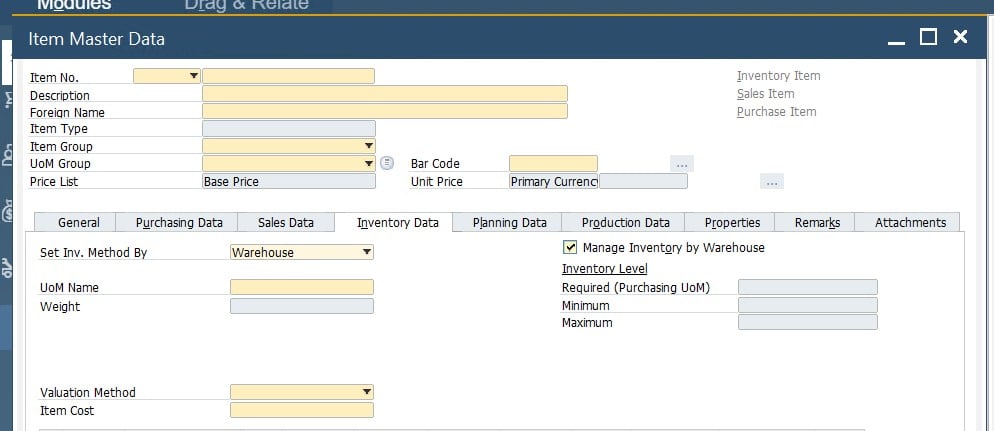
Note that the feature works only with master data records created after it was activated.
Let’s see how to set up predefined values and defaults in SAP Business One. This process happens in four ways:
BP tab. Here, you can adjust various defaults and settings for business partner master data records. For instance, the tab lets you manage credit and commitment limits, payment methods and terms, commissions, dunning terms, approval procedures, etc. These and other parameters are available under Administration/System Initialization/General Settings/BP tab.
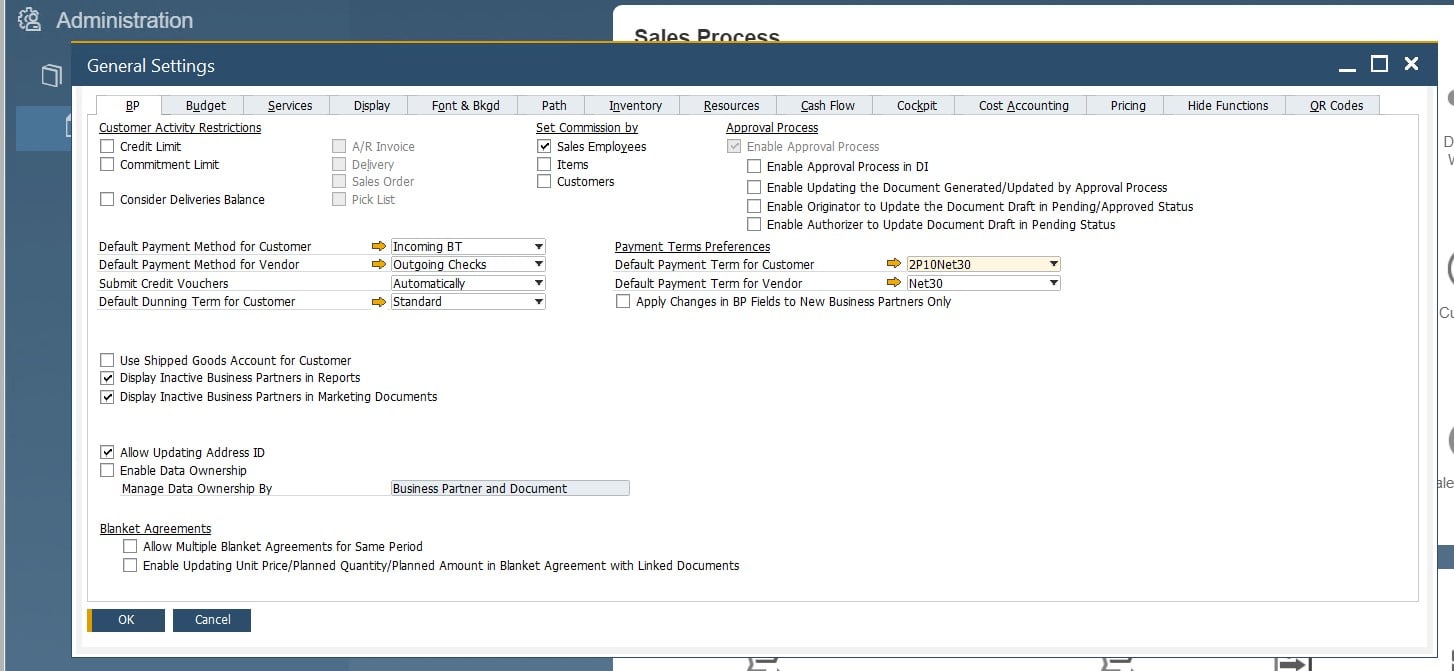
Items tab. This section enables you to work with defaults and settings for reports and documents. You can specify management methods for serial and batch numbers, choose default warehouses for items, and determine whether to show inactive items or not. Go to Administration/System Initialization/General Settings/Inventory tab/Items tab to configure this group of predefined settings and defaults.
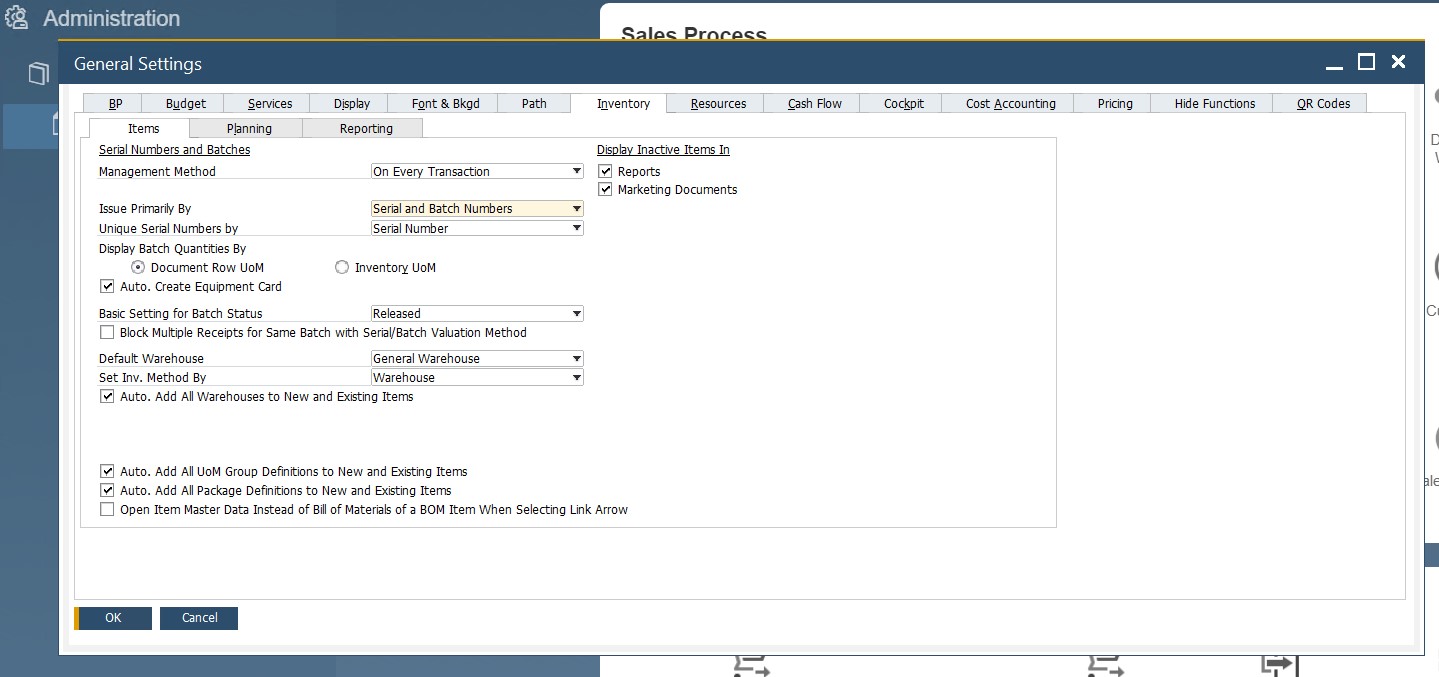
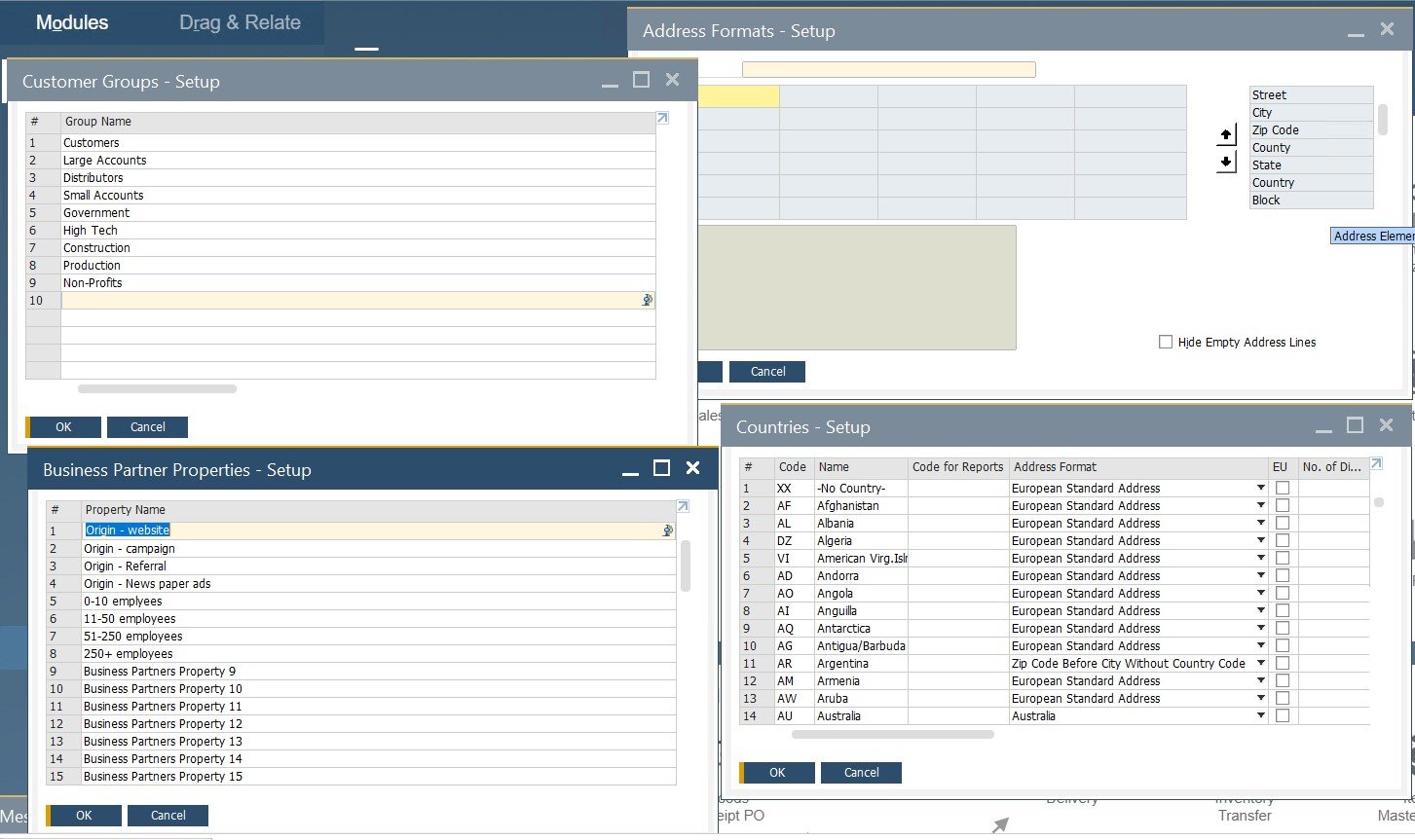
Business Partner screens. The corresponding screens let you configure defaults and predefined values for countries, customer groups, custom properties, vendor groups, sales employees, and address formats. The section is situated under Administration/Setup/Business Partner. Below, you can see four screens related to the section: Customer Groups, Business Partner Properties, Address Formats, and Countries.
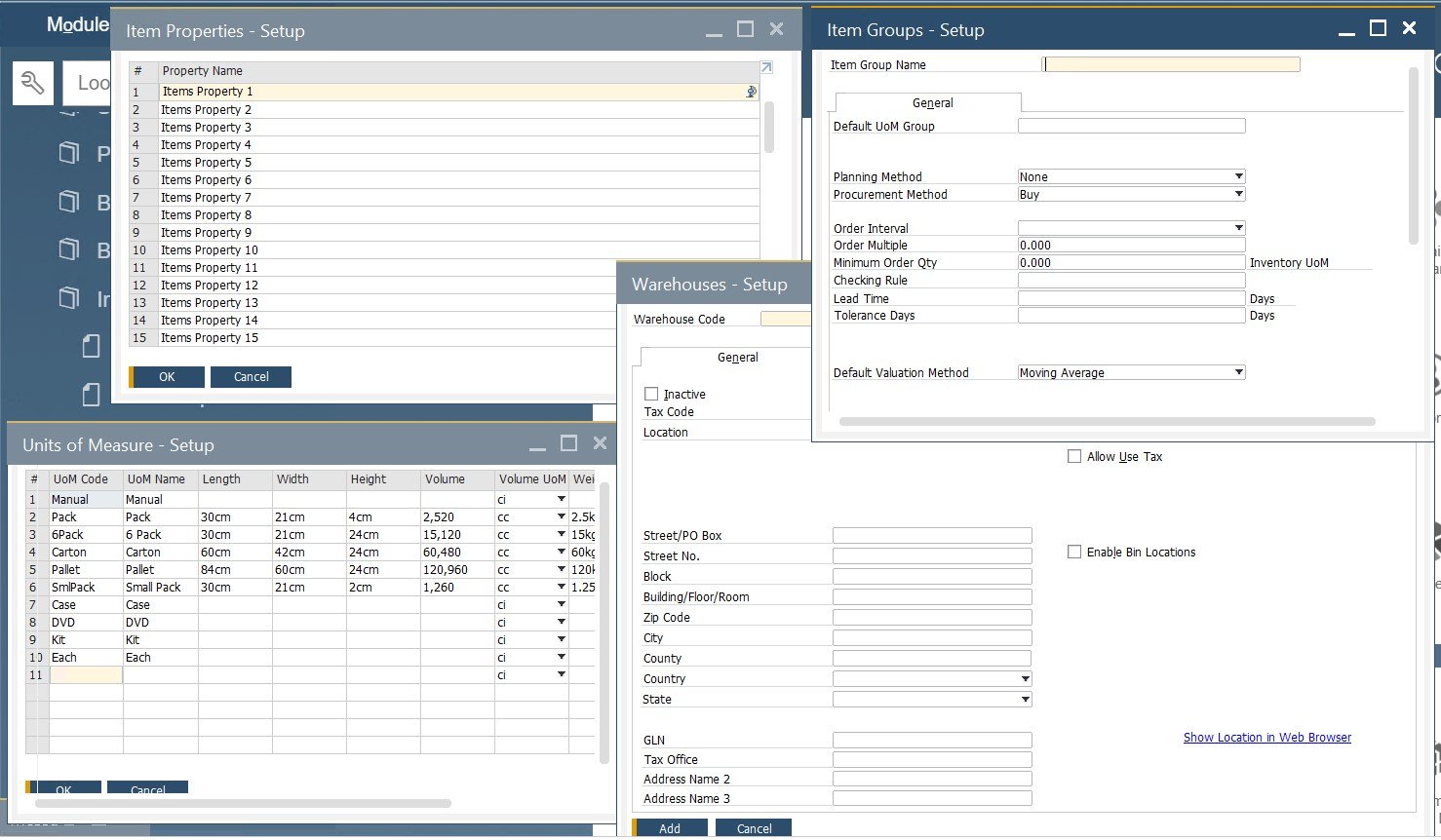
Inventory. SaP B1 lets you configure defaults and predefined values for inventory under Administration/Setup/Inventory. Item groups and properties, warehouses, measurement units, customs groups, cycle count, shipping types, and others are at your disposal. The following four screens are only a part of the Inventory section: Item Properties, Item Groups, Units of Measure, and Warehouses.